Webhook Runbook Conceptual Overviews
Conceptual Overview
The example Webhook Runbook "Webhook Runbook - Simple Example" consists of the following elements:
-
Step-1: Entry-point
-
Runbook
 An automated workflow that executes a series of steps or tasks in response to a triggered event, such as the detection of anomalous behavior generating an incident, a lifecycle event, or a manually executed runbook. node
An automated workflow that executes a series of steps or tasks in response to a triggered event, such as the detection of anomalous behavior generating an incident, a lifecycle event, or a manually executed runbook. node Individual components that make up a runbook automation, each performing a specific function such as data queries, transformations, logic, integrations, or visualizations. Triggering Entity: Webhook links a Riverbed IQ Ops URL to a runbook automation
Individual components that make up a runbook automation, each performing a specific function such as data queries, transformations, logic, integrations, or visualizations. Triggering Entity: Webhook links a Riverbed IQ Ops URL to a runbook automation Automated procedures that are executed as the result of a trigger. Automations consist of a single entry point and a sequence of connected nodes that define the processing logic.. Linking the node to an automation enables the pass-thru of HTTP-request data and context from the calling entity
Automated procedures that are executed as the result of a trigger. Automations consist of a single entry point and a sequence of connected nodes that define the processing logic.. Linking the node to an automation enables the pass-thru of HTTP-request data and context from the calling entity Things deployed in the customer environment that are needed to run the business, such as applications, devices, interfaces, and locations. for further processing.
Things deployed in the customer environment that are needed to run the business, such as applications, devices, interfaces, and locations. for further processing.
-
-
Step-2: Native Data-format
-
Runbook node Variables: Set Primitive Variable parses data and context from the received HTTP-request and stores the data in runbook runtime-variables. Runbook runtime-variables are a native runbook data format which enables the data and context to flow through the Processing Logic
 A runbook node category that adds conditions to branch the runbook, enabling conditional execution paths based on data and context..
A runbook node category that adds conditions to branch the runbook, enabling conditional execution paths based on data and context..
-
-
Step-3: Processing Logic consists of two separate parallel paths of execution.
-
Path-C1: parses the supplied information out of the HTTPS-payload and captures/visualizes the information for the runbook execution in a table.
-
Path-C2: processes the supplied information to discern the associated remediation action.
-
Refer to the diagram below for a visual overview of the runbook.
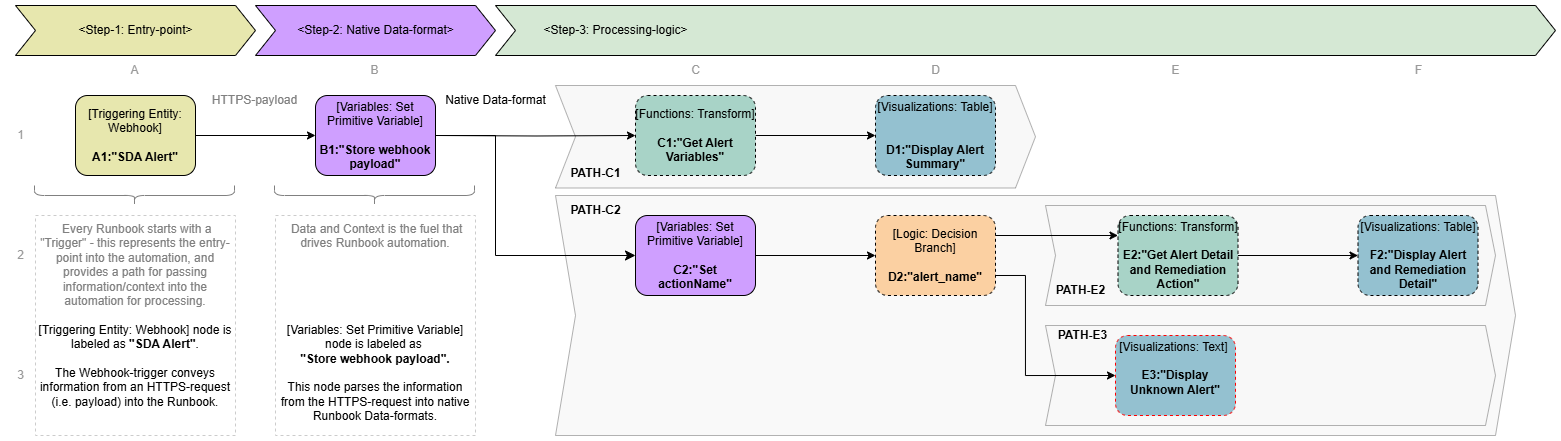
Runbook Overview
The Webhook Runbook Example implementation was built using the following runbook Nodes![]() Individual components that make up a runbook automation, each performing a specific function such as data queries, transformations, logic, integrations, or visualizations. from the palette:
Individual components that make up a runbook automation, each performing a specific function such as data queries, transformations, logic, integrations, or visualizations. from the palette:
-
Entry-point
-
A1: "SDA Alert" - use of runbook Node Triggering Entity: Webhook
-
Label: SDA Alert
-
Purpose: enables linking of a Riverbed IQ Ops URL to this runbook automation and provides for pass-thru of HTTP-request data and context from the calling entity for further processing.
-
-
-
Native Data-format
-
B1: "Store webhook payload" - use of runbook Node Variables: Set Primitive Variable
-
Label: Store webhook payload
-
Purpose: parses data and context from the received HTTP-request and stores the data and context in runbook runtime variables.
-
-
-
Processing Logic: consists of two separate parallel paths of execution.
-
Path-C1: parses the supplied information out of the HTTPS-payload and captures/visualizes
 A runbook node category that shows data in a chart, graph, table, or note, providing visual representation of analysis results in runbook output. the information for this runbook execution in a table.
A runbook node category that shows data in a chart, graph, table, or note, providing visual representation of analysis results in runbook output. the information for this runbook execution in a table.-
C1: "Get Alert Variables" - use of runbook Node Functions: Transform
-
Label: Get Alert Variables
-
Purpose: transforms specified Variables into a JSON format that can be processed by downstream nodes.
-
-
D1: "Display Alert Summary" - use of runbook Node Visualizations: Table
-
Label: Display Alert Summary
-
Purpose: visualizes the supplied Variables (JSON) into a table.
-
-
-
Path-C2: processes the supplied information to discern the associated remediation action (i.e. actionName).
-
C2: "Set actionName" - use of runbook Node Variables: Set Primitive Variable
-
Label: Set actionName
-
Purpose: applies logic to map the supplied Alert to a recommended remediation (i.e. actionName).
-
-
D2: "alert_name" - use of runbook Node Logic: Decision Branch
-
Label: alert_name
-
Purpose: determines whether the supplied Alert is known or unknown and directs path of execution accordingly
-
Path-E2: If the Alert is Known, the runbook continues processing the Alert and associated Remediation.
-
E2: "Get Alert Detail and Remediation Action" - use of runbook Node Functions: Transform
-
Label: Get Alert Detail and Remediation Action
-
Purpose: transforms specified Variables into a JSON format that can be processed by down-stream nodes.
-
-
F2: "Display Alert and Remediation Detail" - use of runbook Node Visualizations: Table
-
Label: Display Alert and Remediation Detail
-
Purpose: visualizes the supplied Variables (JSON) in a table.
-
-
-
Path-E3: If the Alert is Unknown, the runbook stops further processing and logs the Unknown Alert.
-
E3: "Display Unknown Alert" - use of runbook Node Visualizations: Text
-
Label: Display Unknown Alert
-
Purpose: logs the Unknown Alert in text.
-
-
-
-
-
-