Incident Lifecycle Events and Runbooks
Incident![]() A collection of one or more related triggers. Relationships that cause triggers to be combined into incidents include application, location, operating system, or a trigger by itself. lifecycle events indicate the state of ongoing incidents. Incident lifecycle runbooks
A collection of one or more related triggers. Relationships that cause triggers to be combined into incidents include application, location, operating system, or a trigger by itself. lifecycle events indicate the state of ongoing incidents. Incident lifecycle runbooks![]() An automated workflow that executes a series of steps or tasks in response to a triggered event, such as the detection of anomalous behavior generating an incident, a lifecycle event, or a manually executed runbook. provide a tool for tracking incident lifecycle changes, and making that information available outside of Riverbed IQ Ops, through, for example, messaging applications
An automated workflow that executes a series of steps or tasks in response to a triggered event, such as the detection of anomalous behavior generating an incident, a lifecycle event, or a manually executed runbook. provide a tool for tracking incident lifecycle changes, and making that information available outside of Riverbed IQ Ops, through, for example, messaging applications![]() An entity type representing software applications deployed in the customer environment that are monitored for performance and anomalies. and service management applications. Unlike incident runbooks, lifecycle runbooks do not perform analysis or output
An entity type representing software applications deployed in the customer environment that are monitored for performance and anomalies. and service management applications. Unlike incident runbooks, lifecycle runbooks do not perform analysis or output![]() A document containing data sets generated by the execution of a runbook, including output of queries and reports from point products, as well as output of analysis or other runbook nodes. data to visualizations
A document containing data sets generated by the execution of a runbook, including output of queries and reports from point products, as well as output of analysis or other runbook nodes. data to visualizations![]() A runbook node category that gets data about the trigger and forwards it to other nodes in the runbook for further processing. (such as tables and charts) or impact
A runbook node category that gets data about the trigger and forwards it to other nodes in the runbook for further processing. (such as tables and charts) or impact![]() Uniform Resource Locator. The address used to access resources on the internet, such as webhook endpoints or API endpoints for runbook automation. statements. However, you can use notes to record the information that the runbook passes to external recipients.
Uniform Resource Locator. The address used to access resources on the internet, such as webhook endpoints or API endpoints for runbook automation. statements. However, you can use notes to record the information that the runbook passes to external recipients.
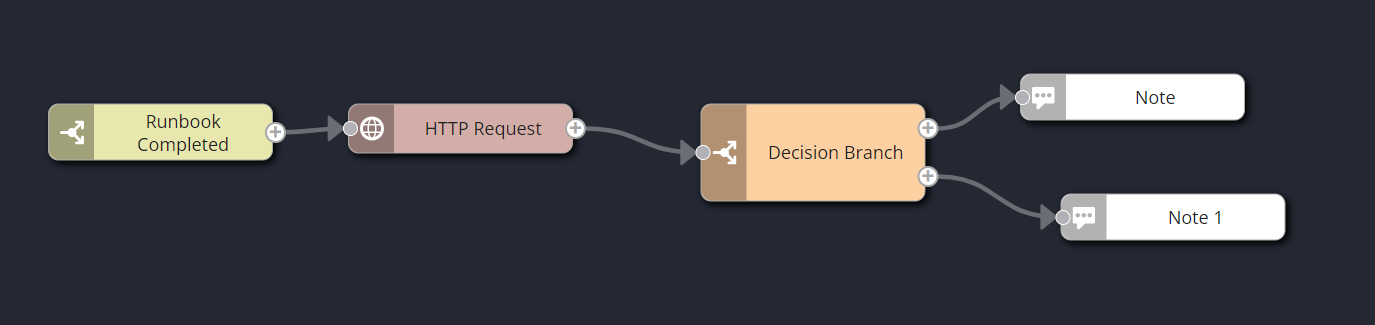
A simple example of a lifecycle runbook follows. This runbook takes the Runbook Completed trigger![]() A set of one or more indicators that have been correlated based on certain relationships, such as time, metric type, application affected, location, or network device. information, posts it to an HTTP
A set of one or more indicators that have been correlated based on certain relationships, such as time, metric type, application affected, location, or network device. information, posts it to an HTTP![]() Hypertext Transfer Protocol. A protocol used for transmitting data over the internet, commonly used in webhook runbooks and integrations with external systems. endpoint, and writes the result in one of two notes: One note for a 200 result code, another note for any other result.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol. A protocol used for transmitting data over the internet, commonly used in webhook runbooks and integrations with external systems. endpoint, and writes the result in one of two notes: One note for a 200 result code, another note for any other result.
Access Lifecycle Runbooks from the Lifecycle Runbooks page.
The Runbook Editor Node![]() Individual components that make up a runbook automation, each performing a specific function such as data queries, transformations, logic, integrations, or visualizations. Palette furnishes these incident lifecycle triggers for defining lifecycle runbooks:
Individual components that make up a runbook automation, each performing a specific function such as data queries, transformations, logic, integrations, or visualizations. Palette furnishes these incident lifecycle triggers for defining lifecycle runbooks:
-
Runbook Completed
-
Note Added
-
Note Updated
-
Ongoing State Changed
The Automation![]() Automated procedures that are executed as the result of a trigger. Automations consist of a single entry point and a sequence of connected nodes that define the processing logic. Management page maps runbooks for these triggering entities
Automated procedures that are executed as the result of a trigger. Automations consist of a single entry point and a sequence of connected nodes that define the processing logic. Management page maps runbooks for these triggering entities![]() Things deployed in the customer environment that are needed to run the business, such as applications, devices, interfaces, and locations.:
Things deployed in the customer environment that are needed to run the business, such as applications, devices, interfaces, and locations.:
-
Impact Analysis Ready
-
Incident Indicators Updated
-
Incident Note Added
-
Incident Status Changed
-
Ongoing Incident Changed